Module 2: Why infrastructure projects are prone to corruption
Ability to conceal corruption: Intermediaries
The payment of a bribe may be made directly by the payer to the ultimate recipient who is to carry out the dishonest act required by the bribe.
However, it is common for a bribe to be paid through an individual or organisation which acts as an intermediary in the transaction.
There are four main types of intermediary used in corrupt circumstances:
- agent
- joint venture partner
- subsidiary
- sub-contractor.
Because these organisations normally wholly or partly carry out legitimate and honest work, it is more difficult to detect if they are acting as corruption intermediaries.
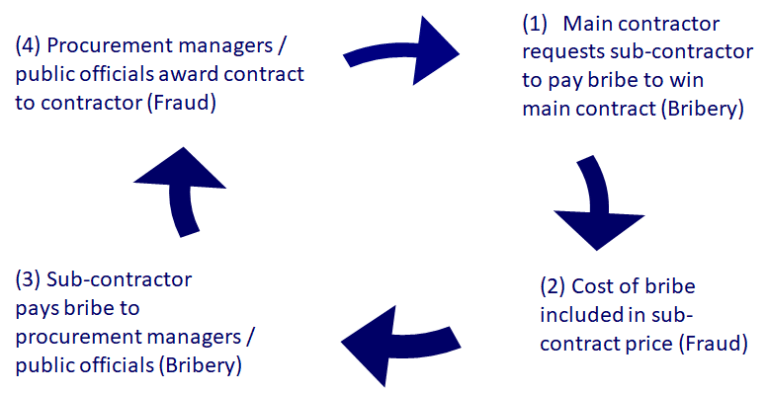
An example of how a main contractor and sub-contractor could conspire to arrange that a bribe is paid by the sub-contractor is shown in the following diagram.
April 2025
© GIACC

